Ear Care EDU
Is Earwax Healthy?
Earwax, also known as cerumen, is a waxy, yellowish substance that is produced by the sebaceous gland within the ear. Cerumen can be found in a number of forms, ranging from liquid, through soft to hard earwax, depending on genetics as well as stress, fear and environmental and climate factors.
Earwax performs an important function as it lubricates, cleans, and protects the lining of the ear canal by repelling water, trapping dirt, and ensuring that insects, fungi, and bacteria do not get through and harm the eardrum.
When Does Earwax Become a Problem?
The human body has a self-cleaning mechanism that utilizes jaw movements to drive excess ear wax through the ear canal and out of the ear. When this mechanism does not function as it should, there is a need for external intervention to routinely and properly remove the extra earwax.
Earwax clogging is more common in warm climates, and is intensified by frequent use of headsets and ear plugs, which prevent ventilation of the ear canal and stimulate earwax production.
Referred to as cerumen impaction, excessive accumulation of earwax can form a plug, and lead to a blocked ear. This widespread phenomenon is experienced by 57% of seniors, 33% of disabled people, 10% of children and 5% of healthy adults.
What Medical Conditions Can Cause Excess Earwax?
Some people have excess earwax, some do not. As we age, it is common to see a rise in earwax production, however there are also health conditions that can lead to overproduction of earwax, which, if not treated, can become impacted and affect hearing and quality of life:
- Bony blockage (osteoma or exostoses)
- Infectious disease, such as swimmer’s ear (external otitis)
- Skin disease (such as eczema)
- Autoimmune disease (such as lupus)
- Narrowed ear canal (from birth, chronic inflammation, or injury)
- Making too much earwax due to injury
(https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/i/impacted-earwax.html)
What Are the Health Risks of Impacted Ear Wax?
Cerumen impaction is the number one cause of various degrees of temporary, treatable hearing loss. Many people are often unaware of partial loss of hearing, which has a direct effect on quality of life, including productivity, frustration, behavioral changes, and even social withdrawal.
In some cases, impacted earwax can cause earache, and in rare cases tinnitus (ringing in the ear) dizziness, and vertigo (loss of balance).
Hearing Aids and Earwax – A Challenging Combination for Audiologists
People wearing hearing aids often complain of an increase in earwax. The reason is that hearing aids may stimulate the glands producing earwax. In fact, earwax blocks 60-80% of hearing aids’ filters, and might damage the microphone resulting in reduced efficacy of the device. In addition, the hearing aids themselves, located in the ear canal, block the wax’s natural exit passage out of the ear.
Cerumen buildup can affect patients even before a hearing aid is fitted. Patients who need a hearing aid fitting and suffer from the presence of earwax cannot have the device fitted at a first appointment are are usually sent out to have their ears cleaned before returning for a fitting. As the pathway to audiology is not completed as planned for both practitioner and patient, there are a number of potential consequences. Most commonly, frustrated patients do not return, resulting in extended reduced hearing and loss of quality of life. The practitioner, in turn, loses contact with patients who do not return for the fitting and do not meet their goal of improving hearing.
The American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery recommend that if you are prone to repeated wax impaction or use hearing aids, you should carry out routine preventive cleaning. It is also important to maintain clean hearing aids.
Current Removal Practices
Over recent decades there have been no significant advances in treating impacted earwax.
The accepted practice is for healthcare professionals to refer patients to Ear, Nose and Throat Specialists, who are currently the only clinicians equipped to treat earwax blockages safely and effectively.
Some patients who undergo earwax removal with complex equipment by an Ear, Nose and Throat specialist, experience varying degrees of discomfort, depending on the extraction method and the physician’s experience.
There is also an array of home remedies that claim to clear earwax. These include ear drops, ear candles, home remedies (olive oil, baking soda, vinegar, glycerine, etc.) and cotton swabs. At best, most of these are ineffective; at worst, they can cause severe clinical damage such as eardrum perforation. Some methods, such as using cotton swabs in the ear, have even been banned by official regulatory organizations, due to the danger.
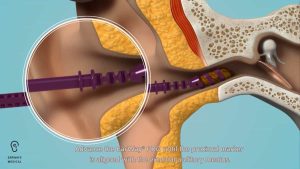
EarWays: A Game Changer in Earwax Removal
Cone-shaped spiral tools simply don’t work at removing impacted earwax, and can cause wax to be pushed further into the ear canal. The helical head of the both the EarWay Pro and EarWay contains a cavity designed to capture earwax in one go without pushing it closer to the eardrum. Using EarWay to remove impacted earwax increases patient satisfaction, and reduces delays in care.
Open Profile Helix Structure
- Unique, patented open profile
- Separation from the ear canal
- Engulfs the wax plug and holds it firmly
- Pulling out in a single cluster
- Coated for maximum comfort.